Private Clouds Federation¶
This section provides a guide of how to Federate a private Openstack Cloud with a central Keyrock-based FIWARE Environment. Using this kind of configuration, an external Openstack Cloud can offer part of its resources to the FIWARE Lab users.
Main Concepts¶
The scenario¶
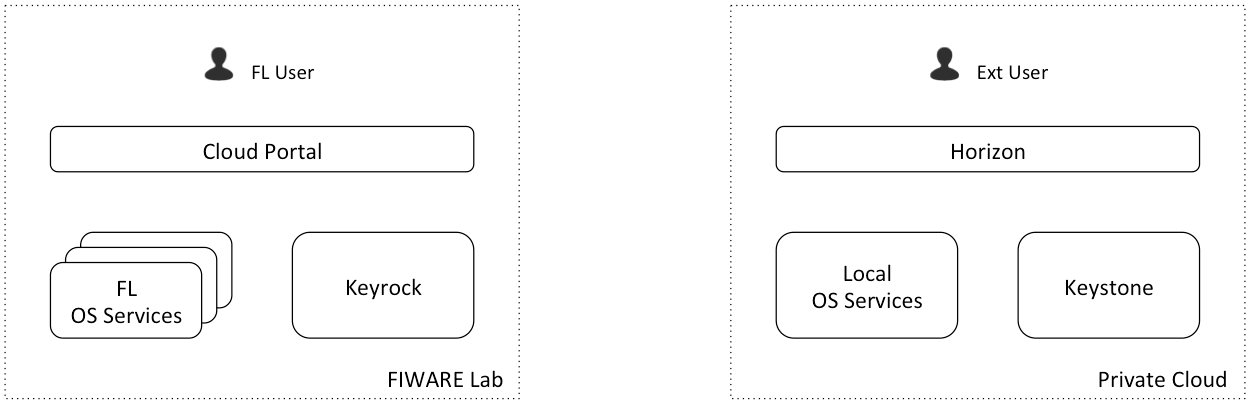
- FL user represents a user with a registered account in FIWARE Lab
- In FIWARE Lab environment, FL OS Services represent the services of all the Federated nodes
- Private Cloud wants to offer some of its resources (part of Local OS Services) to be available in FIWARE Lab as a new node.
- Private Cloud has their own users registered in its local Keystone (Ext User is one of them) and using Cloud resources deployed in Local OS Services
Espected Behaviour¶
- Ext User can continue using his deployed resources in Local OS Services using Horizon
- FL User (if he has the correct rights) can deploy resources in Private Cloud Local OS Services using Cloud Portal
- In Cloud Portal, Private Cloud node appears as a new node. It is accessible for FIWARE Lab users with quotas in that node (community users assigned to that node)
- Private Cloud infrastructure owners can assign quotas of Local OS Services to FIWARE Lab users
- FL User can continue using FL OS Services as before.
- If a Ext User wants to use FIWARE Lab nodes resources, he has to create an account in FIWARE Lab.
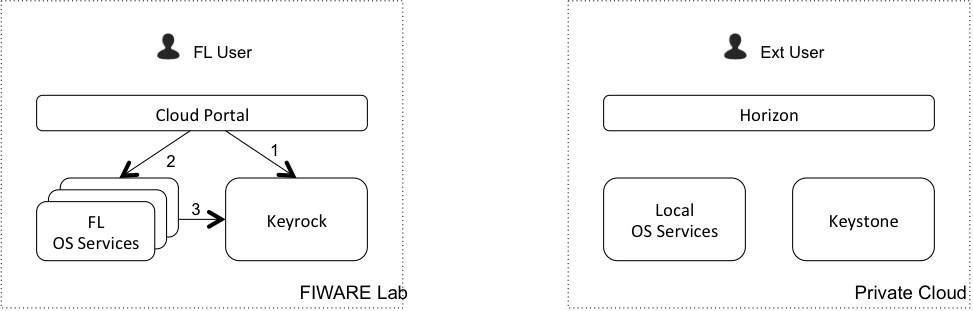
FL User using FIWARE Lab resources¶
- Cloud Portal authenticates the user in Keyrock
- Cloud Portal sends a request to an OS Service
- OS Service validates the token with Keyrock
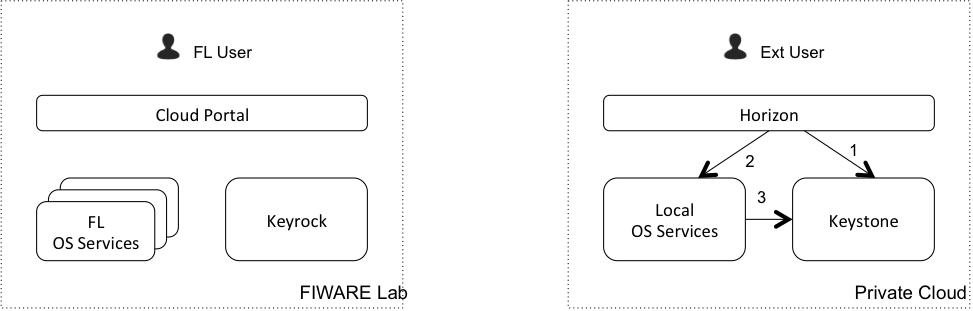
Ext User using Local resources¶
- Horizon authenticates the user in Keystone
- Horizon sends a request to an OS Service
- OS Service validates the token with Keystone
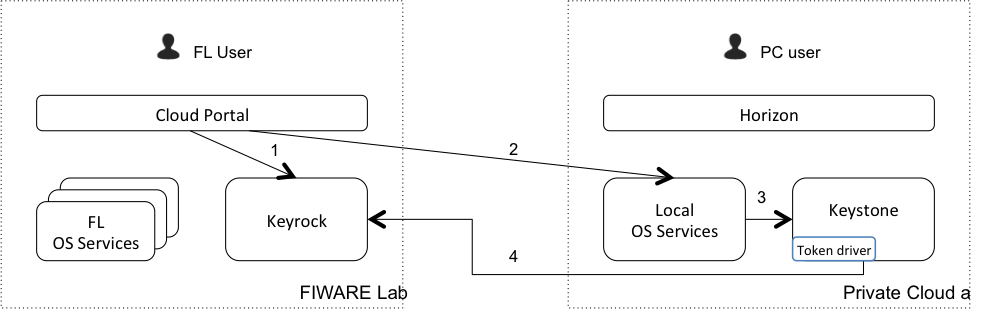
FL User using Private Cloud resources¶
- Cloud Portal authenticates the user in Keyrock
- Cloud Portal sends a request to a Private Cloud OS Service
- Private Cloud OS Service tries to validate the token in Keystone
- As the validation doesn’t success (the token is not stored in Keystone), Keystone validates it with Keyrock acting as a gateway and sending the response to Private Cloud OS Service
*. If the validation success, Keystone stores the token locally (in cache), so the next times the step 4 is not required.
Installation and Configuration¶
To have a compatible Keystone in your Private node you have to install a modified version of this component. This version is available here
This modified Keystone includes an implementation of the described Token Driver. You can install it as a regular Keystone. To configure the Token Driver you have only to add the information about the central FIWARE Lab Keyrock instance in the Keystone configuration file:
[simplefederation]
idp=http://user1:password1@idp1.provider1.test:35357
idp=http://user2:password2@idp2.provider2.test:35357
The configured users needs admin permissions in the central Keystone to be able to validate tokens there.
A detailed installation and configuration guide can be found here